Antioxidant Activity Comparison of Ethyl Acetate Extract of Gandaria Stem Bark Using DPPH and ABTS Methods
Keywords:
Bouea macrophylla, antioxidant, gandariaAbstract
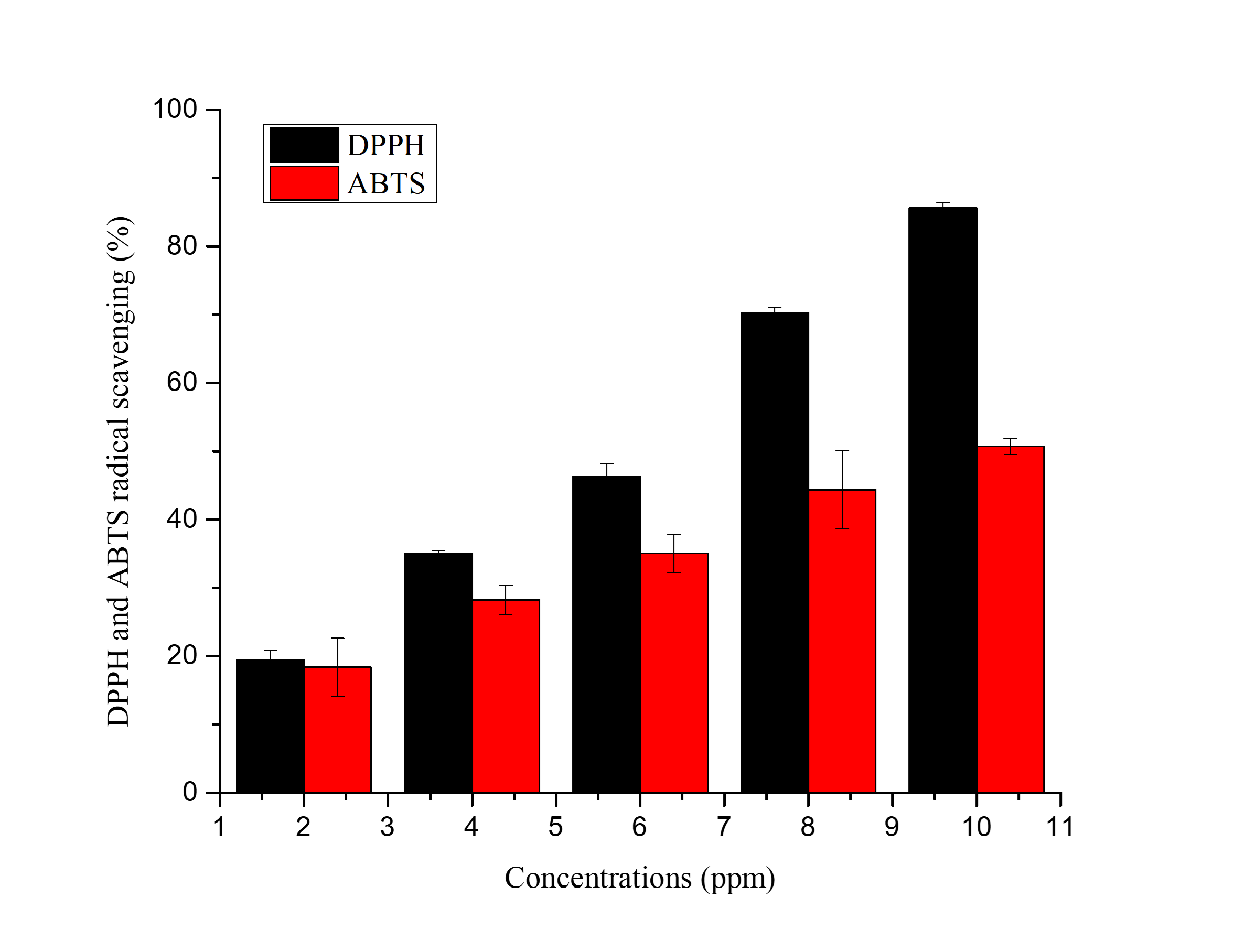
This study aimed to evaluate and compare the antioxidant activity of ethyl acetate extract of Bouea macrophylla (Gandaria) stem bark using DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) and ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonate)) free radical scavenging methods. The extraction was performed by maceration using ethyl acetate as the solvent, yielding 16.7 g of concentrated extract with an extraction yield exceeding 10%, indicating efficient solvent penetration and metabolite recovery. The antioxidant activity was measured at concentrations of 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 ppm, and the IC50 value was calculated for each method. The DPPH method showed a higher antioxidant activity with an IC50 value of 5.837 ± 0.060 ppm, while the ABTS method yielded an IC50 of 9.645 ± 0.697 ppm. These results indicate that the extract possesses strong antioxidant potential, likely due to the presence of secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, tannins, and polyphenols. The findings suggest that Gandaria stem bark extract could serve as a promising natural antioxidant source for pharmaceutical or nutraceutical applications
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Nurhayati Bialangi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.











